Old maintenance practices, and most of the current ones, both in the private sector as well as in the public sector, are usually understood as activities related to equipment reparation after a break down. Webster’s definition of maintaining is “to keep in an existing state, preserve from failure”. This implies that maintenance must consist of actions taken to prevent an equipment or facility of failing, keeping them in good work condition. Sadly enough, data obtained in numerous studies from the last decade show that most companies do not invest enough resources to keep their equipment and facilities in good condition. On the contrary, they wait until they break down to take the corrective measures needed to repair or replace the equipment. Nothing lasts forever and every piece of equipment has its lifecycle. For example, an equipment can be design to last for 5,000 hours, but with a proper use and maintenance it could last for 10,000 hours.
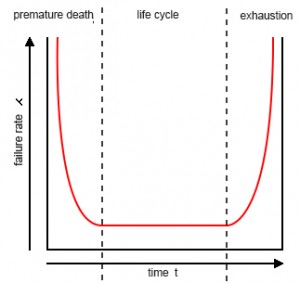
The need of maintenance is based on the actual or imminent fail. Ideally, maintenance is carried out to keep equipment and systems running efficiently during at least its usual life cycle. As such, practical functioning of equipment is a function based on time. If you want to graphically represent the failure rate of a piece of equipment in relation to time, it is probable that the graphic takes the shape of a bathtub, such as the one shown in picture 1, where axis Y represents the failure rate and axis X represents time. This curve can be divided in three periods: premature dead, lifecycle and exhaustion period.
The first period, the premature dead one, of the curve is characterized by a high rate of failure, followed by a decreasing failure period. Most of the failures related at this time are linked to bad design, bad installation or wrong use. The premature dead period is followed by a period with a nearly constant failure rate know as life cycle. There are many theories about why equipment fails in this time area. Most of them agree that poor preventive maintenance has often a key role. It is also generally agreed that exceptional practices related to predictive and preventive maintenance can extend this period in time. Exhaustion period is characterized by a higher and higher rate of failure. In most cases, this period includes a regular distribution of failures during design life but in reverse.
The lifecycle of most of equipment needs periodical maintenance. If we use the example of a car, we could say that filters must be changed, front-end alignment must be maintained, oil change and proper lubrication are needed and so on. In some cases, certain pieces need to be replaced, for example, the timing belt, to ensure the proper functioning of the main piece of the equipment, the car in this particular case, once its design life has ended. Each time we do not carry out the maintenance activities planned by the designer, we shorten the operational lifecycle of the equipment. So, what are our options? For the last 20-30 years the different approaches to how maintenance can be carried out to ensure that the equipment reaches or exceeds its design life are focused on proactivity, thus, on a proper preventive maintenance and more and more on preventive maintenance accompanied by proper predictive maintenance to complement it.
And now, we will show the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of maintenance:
CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE
Advantages:
- Low cost
- Fewer workers needed
Disadvantages:
- Costs increase due to unplanned equipment stops
- Labour costs increase, especially when extra time is needed
- Extra costs due to equipment repair or replacement
- Secondary equipment can suffer damage during primary equipment failure
- Inefficient use of human resources
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Advantages:
- Inactivity time gets shorten, so equipment availability increases
- Maintenance regularity allows better flexibility
- Components life cycle extends
- Energy savings
- Failure rate decreases
- Costs reduction around 12-18% in comparison with corrective maintenance
Disadvantages:
- It is still probable that failure happens
- Intensive workforce
- It includes activities that may not be really necessary but recommended
- These activities that may not be necessary may accidentally cause damage to other components
PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE
Advantages:
- Components availability and lifetime increases
- Equipment inactivity time decreases
- Materials and labour costs decrease
- Improves employees’ spirits
- Costs reduction around 8-12% in comparison with preventive maintenance
Disadvantages:
- Significant initial investment in diagnosis equipment
- Investment in personnel training increases
- Potential savings are not easily perceived by the C-Suite
- Meaningful savings are only perceived in the long term